HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language, and it is the most widely used language to write Web Pages.
- Hypertext refers to the way in which Web pages (HTML documents) are linked together. Thus, the link available on a webpage is called Hypertext.
-
As its name suggests, HTML is a Markup Language which means you use HTML to simply “mark-up” a text document with tags that tell a Web browser how to structure it to display.
-
It is static language i.e. it does not change at run time.
-
It is used for web designing i.i. how to design front page of website
We use predefined tags
Tag:- A tag is specified and bounded area which is used to perform any specific task and already encode into any browser library know as tag.
First example of html:-
Html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>html</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
OUTPUT:-
This is a Heading
This is a paragraph.
Example Explained
- The
declaration defines this document to be HTML5 - The
element is the root element of an HTML page - The
element contains meta information about the document - The
element specifies a title for the document - The
element contains the visible page content - The
element defines a large heading
- The
HTML Tables:-
Example:-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><table style=”width:100%”>
<tr>
<th>Firstname</th>
<th>Lastname</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Jill</td>
<td>Smith</td>
<td>50</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Eve</td>
<td>Jackson</td>
<td>94</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John</td>
<td>Doe</td>
<td>80</td>
</tr>
</table></body>
</html>
OUTPUT:-
| Firstname | Lastname | Age |
|---|---|---|
| Jill | Smith | 50 |
| Eve | Jackson | 94 |
| John | Doe | 80 |
HTML Forms:-
Example:-
First name:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body><form action=”/action_page.php”>
First name:<br>
<input type=”text” name=”firstname” value=”Mickey”>
<br>
Last name:<br>
<input type=”text” name=”lastname” value=”Mouse”>
<br><br>
<input type=”submit” value=”Submit”>
</form>
</body>
</html>
OUTPUT:-
First name:
Last name:
HTML5 (total 90 tags):-
2 types:-
- Paired tag:-<html></html>
- Unpaired tag:-<br>,<hr>,<input>,<link>
We call html as markup language because we use markup tags i.e. inbuild tag.
Example:-
This example adds a new element called to an HTML page, and defines a style for it:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
document.createElement(“myHero”)
<style>
myHero {
display: block;
background-color: #dddddd;
padding: 50px;
font-size: 30px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><h1>A Heading</h1>
<myHero>My Hero Element</myHero></body>
</html>
OUTPUT:-
A Heading
My Hero Element
New Semantic Elements in HTML5
Many web sites contain HTML code like:
HTML5 offers new semantic elements to define different parts of a web page:
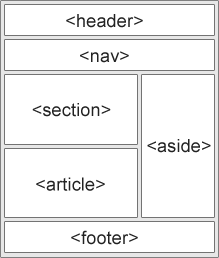
Difference between GET and POST:-
GET:-
- When we use get method than everyone can see the parameter value on the addressbar.
- It is not secure.
- It takes small files.
- Only 2kb data it takes.
POST:-
- When we use post method than no one can see the parameter value on the addressbar.
- It is secure than GET.
- It takes the small file as well as large files.
- It breaks the large files into small packets.
Div:-
- The
tag defines a division or a section in an HTML document.
- The
tag is used to group block-elements to format them with CSS
Example:–
This is some text.
This is a heading in a div element
This is some text in a div element.
<p>This is some text.</p>
</body>
</html>
OUTPUT:-
This is some text.
This is a heading in a div element
This is some text in a div element.
This is some text.
Example:-
slidebar1slidebar2footer
Ouptut:-

Example:-
<form action=”b.html” methos=post>
user<input type=”text” name=”t1″ size=50 maxlength=6 placeholder=”enter” value=”click” required><br>
<br>password<input type=”password”>
<br>
<br>gender<input type=”radio”name=”gender” value=”max”>male
<input type=”radio”name=”gender” value=”max”>female
<br><br>
<input type=”checkbox”name=”c1″ value=”check”>Check terms and conditions
<br><br>
email<input type=email><br>
<br>numbers<input type=number><br>
<br>range<input type=range><br>
<br>date<input type=date><br>
<br>color<input type=color><br>
<br><input type=”submit”value=”submit”><br>
<br><input type=reset><br>
</form>
<br><br>
<table>
<tr><th>user</th>
<th><input type=”text”></th>
</tr><br><select
<option>java</option>
<option>php</option>
<option>c</option>
<option>c++</option>
</select>
OUTPUT:-

What is SVG?
- SVG stands for Scalable Vector Graphics
- SVG is used to define graphics for the Web
The HTML <svg> Element
- The HTML <svg> element is a container for SVG graphics.
- SVG has several methods for drawing paths, boxes, circles, text, and graphic images.
Example:-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body><svg width=”100″ height=”100″>
<circle cx=”50″ cy=”50″ r=”40″
stroke=”green” stroke-width=”4″ fill=”yellow” />
Sorry, your browser does not support inline SVG.
</svg></body>
</html>
Output:-

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body><svg width=”400″ height=”180″>
<rect x=”50″ y=”20″ rx=”20″ ry=”20″ width=”150″ height=”150″
style=”fill:red;stroke:black;stroke-width:5;opacity:0.5″ />
Sorry, your browser does not support inline SVG.
</svg></body>
</html>
Output:-

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body><svg width=”300″ height=”200″>
<polygon points=”100,10 40,198 190,78 10,78 160,198″
style=”fill:lime;stroke:purple;stroke-width:5;fill-rule:evenodd;” />
Sorry, your browser does not support inline SVG.
</svg></body>
</html>
Output:-

MARK:-
- The <mark> tag defines marked text.
- Use the <mark> tag if you want to highlight parts of your text.
Example:-
<pre>welcome</pre>
<pre>w
e
l
c
o
m
e
</pre>
Output:-

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
mark {
background-color: yellow;
color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body><p>A mark element is displayed like this:</p>
<mark>Highlighted text!!</mark>
<p>Change the default CSS settings to see the effect.</p>
<p><strong>Note:</strong> The mark tag is not supported in Internet Explorer 8 and earlier versions.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:-
A mark element is displayed like this:
Highlighted text!!
Change the default CSS settings to see the effect.
Note: The mark tag is not supported in Internet Explorer 8 and earlier versions.